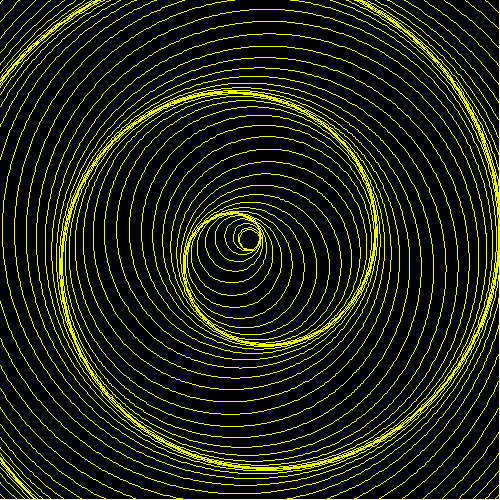
Archimedean Spiral

History
Studied by Archimedes (~287 BC to ~212 BC).
The reason parabolic spiral and hyperbolic spiral are so named is because their equation in polar system r*θ == 1 and r^2 == θ resembles the equation for hyperbola x*y == 1 and parabola x^2 == y in rectangular coordinates system. What is Fermat's involvement with parabolic spiral?
Hyperbolic spiral is also called reciprocal spiral, because it is the inverse curve of Archemedes' spiral, with inversion center at the center. The inversion curve of all Archemedean spirals with respect to a circle on center is another Archemedean spiral. (see below)
Description
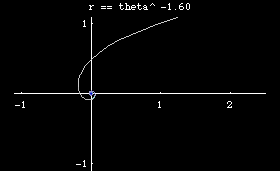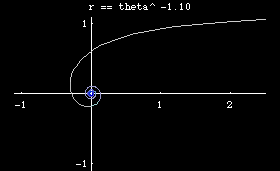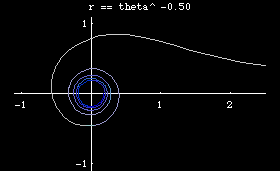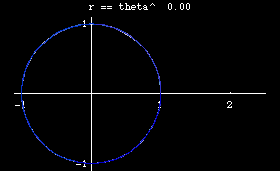
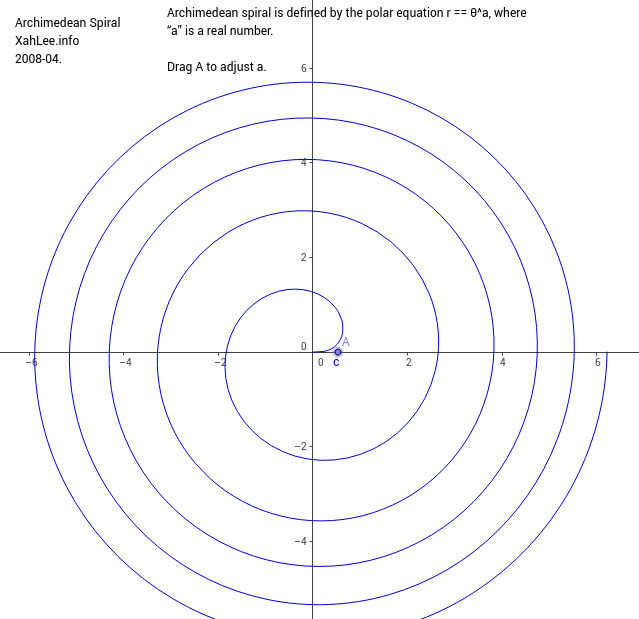
Archimedean spiral is defined by the polar equation r == θ^n. Special names are given for some value of n.
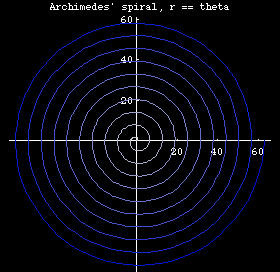
- n == 1, we have r == θ, Archimedes' spiral.
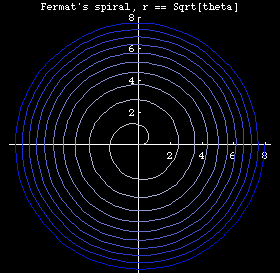
- n== 1/2, we have r == Sqrt[θ], Fermat's spiral. (aka parabolic spiral)
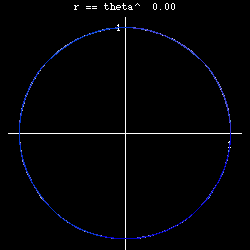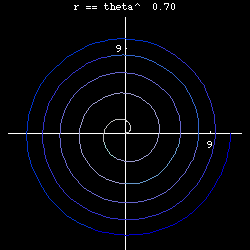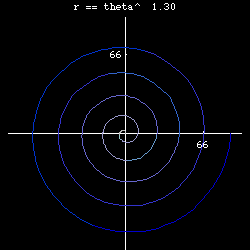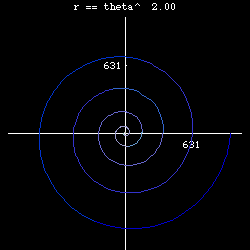
- n== 0, we have r = 1, circle.
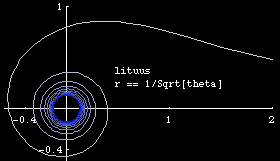
- n== -1/2, we have r == 1/Sqrt[θ], Lituus.
- n== -1, we have r = 1/θ, reciprocal spiral. (aka hyperbolic spiral.)

Formula
- Polar equation: r == θ^n
- Rectangular, Parametric: t^n*{Cos[t],Sin[t]}
Properties
Inversion
The inverse curve of a Archimedean spiral with respect to the center is another Archimedean spiral scaled. Archimedean spiral in parametric form is {t^n*Cos[t], t^n*Sin[t]}. The inversion at origin with radius b of a point {x,y} is {(b^2*x)/(x^2 + y^2), (b^2*y)/(x^2 + y^2)}. Apply this to the parametric form and simply we get b^2*{Cos[t]*t^-n, Sin[t]*t^-n}, which is in polar form r==b^2*θ^(-n). When b==1, there is no scaling.
The inverse curve of Archimedes' spiral with inversion circle of radius 1 at center is the reciprocal spiral.
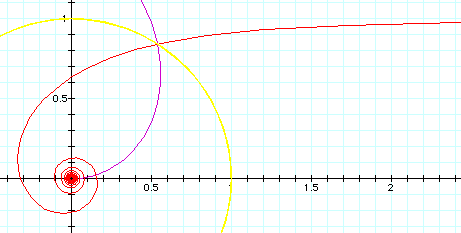
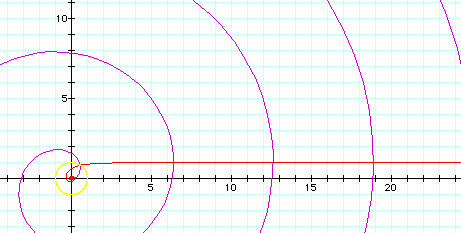
The inverse curve of Fermat's spiral with inversion circle of radius 1 at center is the lituus .
Nested Tangent Circles
The tangent circles of Archimedes's spiral are all nested. need to proof that archimedes spiral's osculating circles are nested inside each other.