Xah Talk Show 2025-06-02 Ep662 Wolfram Language Explore Machine Learning Features
timestamp
- 5:59 Stephen Wolfram on ChatGPT
- 8:53 grok voice chat demo
- 13:23 twitter spam bots
- 14:36 Wolfram Alpha demo
- 18:03 Neural Network Universal Approximation Theorem
- 21:45 grok write tutorial on kotlin
- 27:58 Wolfram Alpha in Mathematica
- 34:02 7k function builtin Wolfram language
- 36:55 Wolfram language doc intro
- 44:12 cryptography demo
- 52:48 graph layout demo
- 53:37 plot 3d demo
- 55:11 machine learning
- 59:00 machine learning classify demo
- 01:16:32 command line repl vs notebook
Video Summary (AI generated)
This video, “Ep662 Wolfram Language. Explore Machine Learning Features. Voice Chat with Grok. Limits of AI,” by Xah Lee, explores various aspects of the Wolfram Language, focusing on its machine learning and AI capabilities.
The speaker also shares his insights and demonstrations of AI chatbots, particularly Grok.
Here's a summary of the key topics:
- Wolfram Language Overview (0:21-1:48): The video begins with an introduction to the Wolfram Language, highlighting its comprehensive nature with over 7,000 built-in functions, which the speaker likens to having an "entire military included" compared to Python's "batteries included" philosophy.
- Wolfram Alpha vs. AI Chatbots (2:43-3:47): The speaker explains Wolfram Alpha as a computational query engine that computes and finds answers from its database, distinguishing it from web search engines like Google and modern AI chatbots.
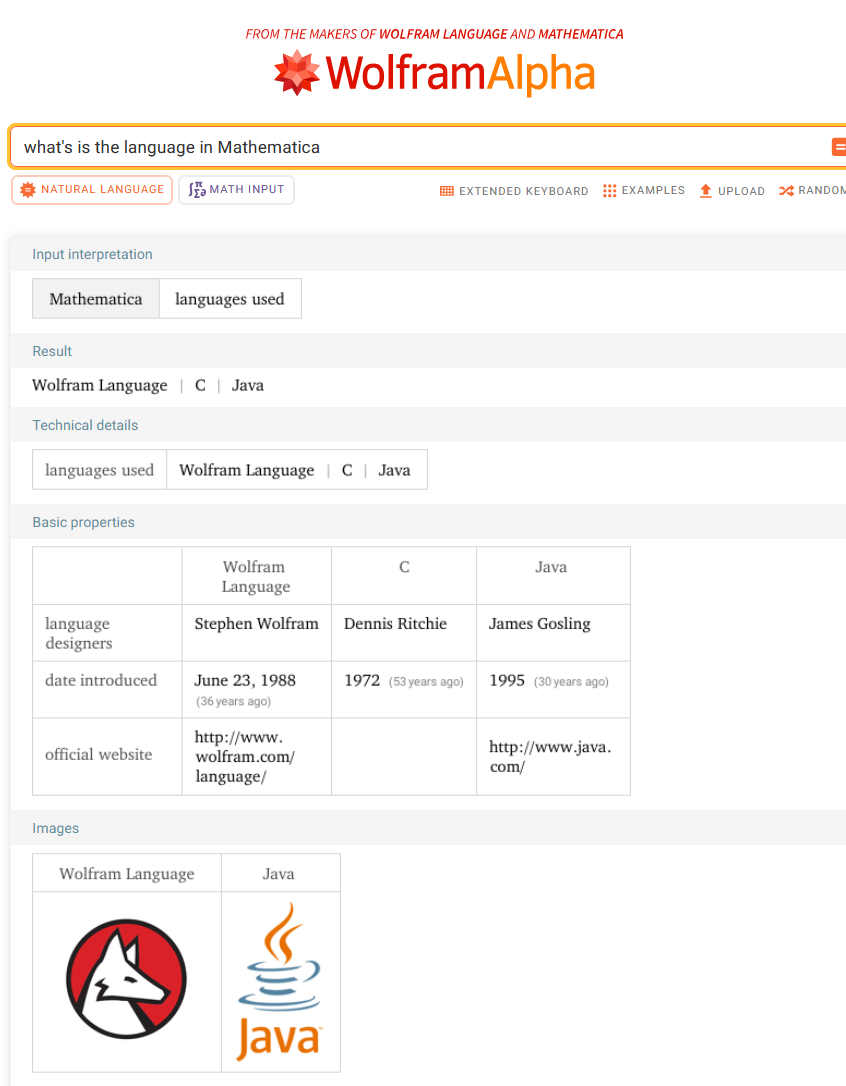
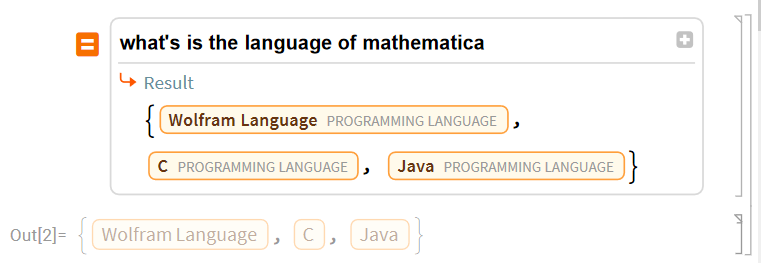
- Rise of AI Chatbots and Grok Voice Demo (3:47-12:10): The video delves into the rise of AI chatbots, with a strong recommendation for Grok. A significant portion of the video is dedicated to a live voice chat demonstration with Grok, showcasing its human-like conversational abilities and its capacity to answer programming-related questions, like identifying the programming language used in Mathematica.
- Stephen Wolfram on ChatGPT (5:59-7:45): The speaker highly recommends Stephen Wolfram's in-depth article on ChatGPT, emphasizing that it explains how the chatbot works rather than just how to code it, offering a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms.
- Neural Network Universal Approximation Theorem (18:03-21:45): The video touches upon the theoretical limits of neural networks, explaining that the Universal Approximation Theorem suggests AI can answer anything known to human knowledge, but in an approximate, statistical manner. The speaker further clarifies that neural networks are essentially complex nested matrix multiplications.
- Grok Writes a Kotlin Tutorial (21:45-24:20): As a practical demonstration of AI's utility, the speaker shows how Grok can generate a simple tutorial on the Kotlin programming language on the spot, highlighting its value for quickly understanding new programming languages.
- Wolfram Alpha in Mathematica (27:58-30:20): The speaker demonstrates how Wolfram Alpha functionality is integrated within the Wolfram Language environment, allowing users to ask questions and receive computational answers directly within Mathematica.
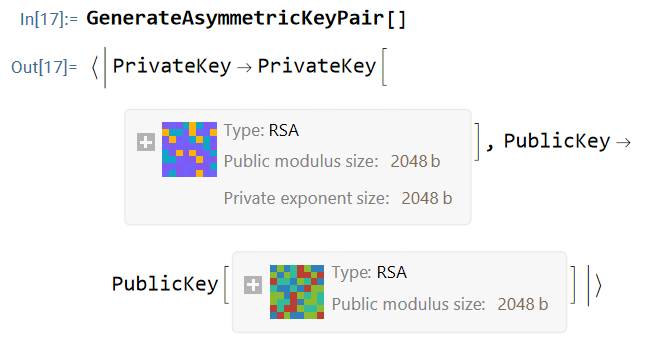
- Wolfram Language Documentation and Features (34:02-55:11): The video explores the extensive documentation of the Wolfram Language, showcasing its vast array of built-in functions (over 7,000). The speaker navigates through various sections, including functional programming, cryptography (44:12), graph layout (52:48), and 3D plotting (53:37), demonstrating the language's symbolic computation capabilities.
- Machine Learning in Wolfram Language (55:11-59:18): The video concludes by exploring the machine learning features within the Wolfram Language, including its capabilities for classification, regression, and clustering, and mentioning the relatively new and experimental LLM-related functionalities introduced in 2023.
- wolfram alpha, how it diff from search engine, and ai chat bots
- the rise of ai chat bots, e.g. chatgpt
- AI: Stephen Wolfram on ChatGPT (2023)
- demo grok voice chat
- AI: Neural Network Tutorial (2023)
- Neural Network and The Universal Approximation Theorem
- grok wrote a simple tutorial on kotlin programing language
- https://x.com/i/grok/share/NBlhBPVG2cyMgyuXDUESwoJxi
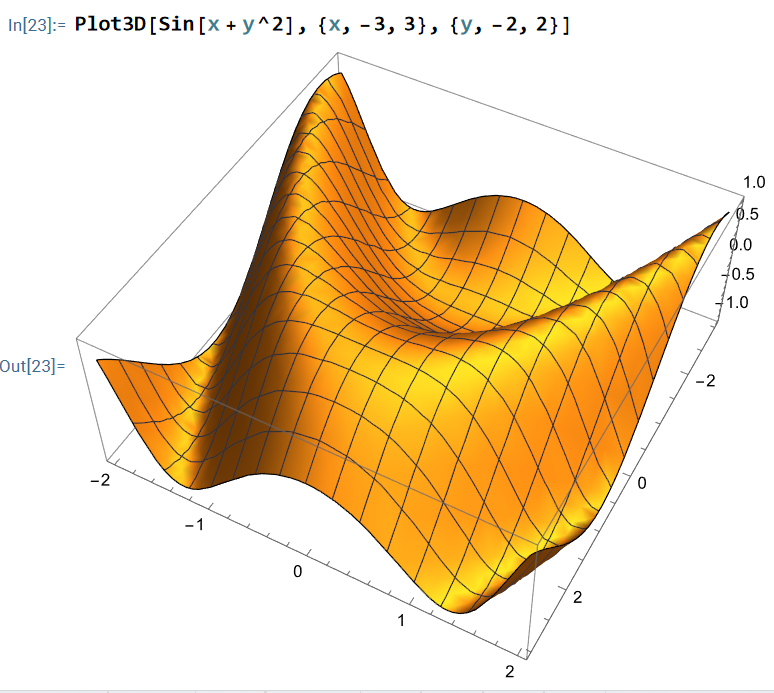
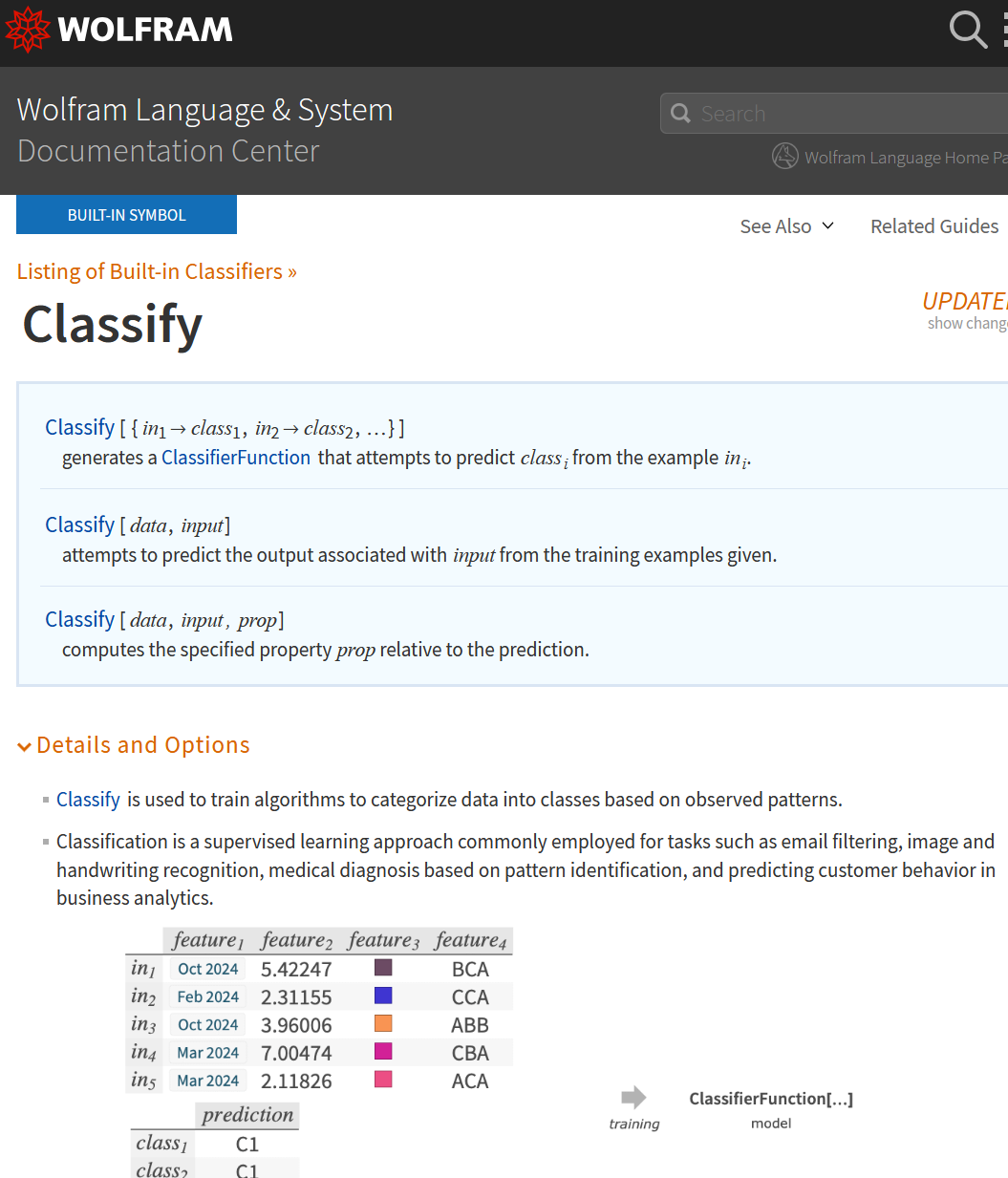
(* demo the classify machine learning function *) (* generate a list of random numbers between 0 and 10 *) xRandomList = Table[ RandomInteger[{0,10}] , {10}] (* {8, 0, 9, 1, 9, 9, 5, 3, 8, 10} *) (* now create a list of pairs, if number is less than 5, lable it small, if it is greater or equal than 5, label it big. *) xData = Map[ Function[x, If[ x < 5, x -> "small", x -> "big"]] , xRandomList] (* {1 -> small, 10 -> big, 1 -> small, 7 -> big, 7 -> big, 0 -> small, 9 -> big, 1 -> small, 7 -> big, 6 -> big} *) xclassifyFun = Classify[xData]; xclassifyFun[3] (* | Time elapsed: | Training example used: | Current best method: | Current accuracy: | Current loss: | | 3.7s | 8/10 | LogisticRegression | 0.833 | 0.235 | small *)