Windows: Networking Commands Tutorial
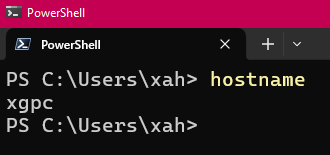
Show Host Name
hostname
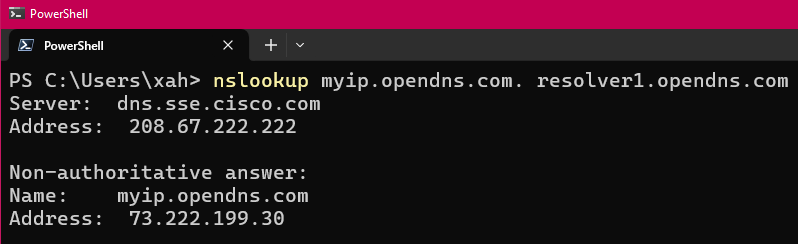
Show My Public IP Address
nslookup myip.opendns.com. resolver1.opendns.com
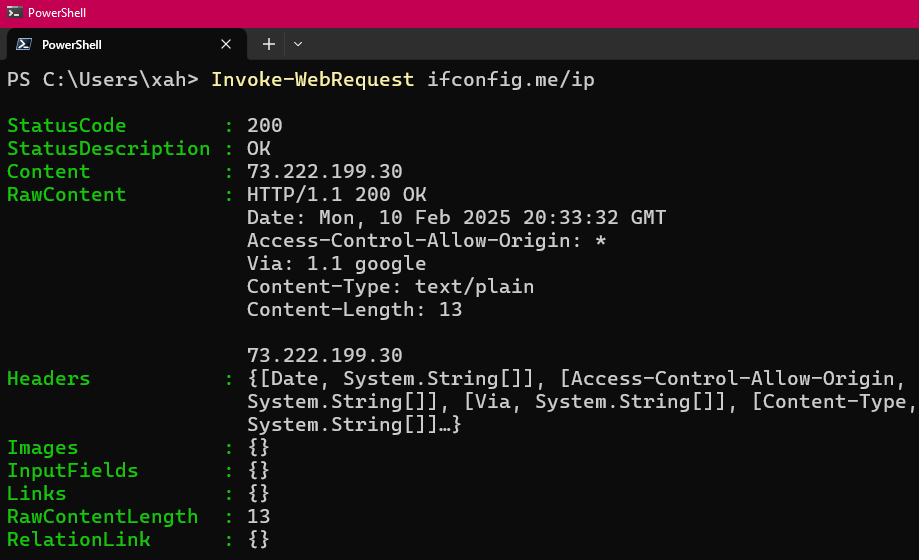
Invoke-WebRequest ifconfig.me/ip
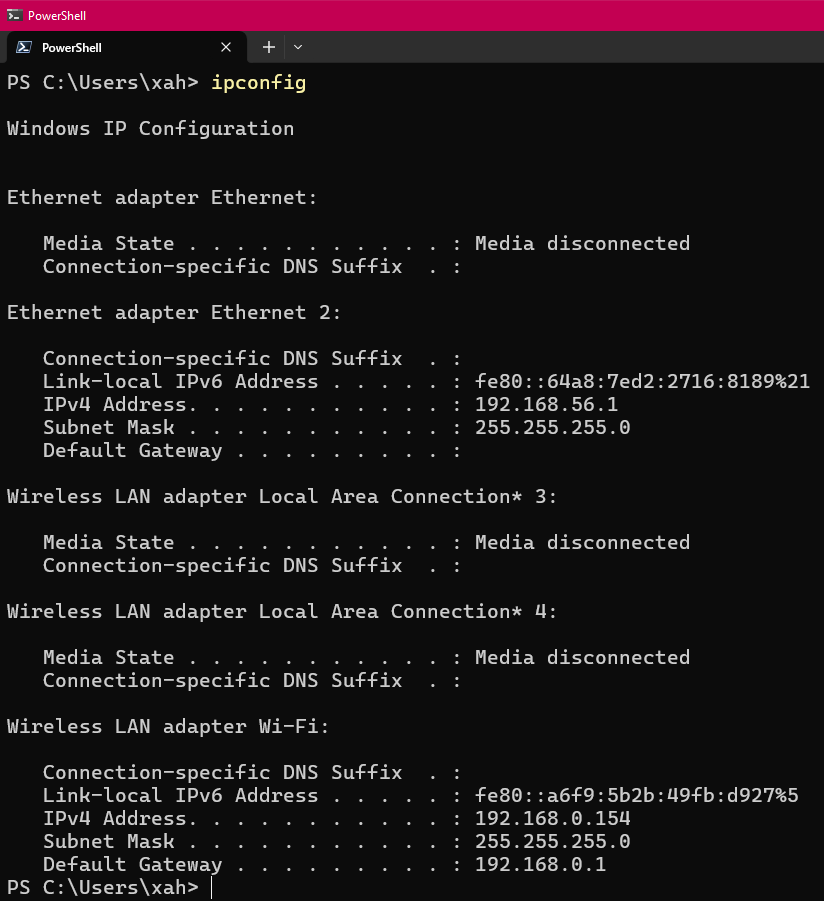
Show IP Address of Network Adapter
ipconfig
The line IPv6 and IPv4 are your IP addresses (for that network adapter).
Show IP Address of Router
ipconfig
the “Default Gateway” line contains your router's IP address.
or
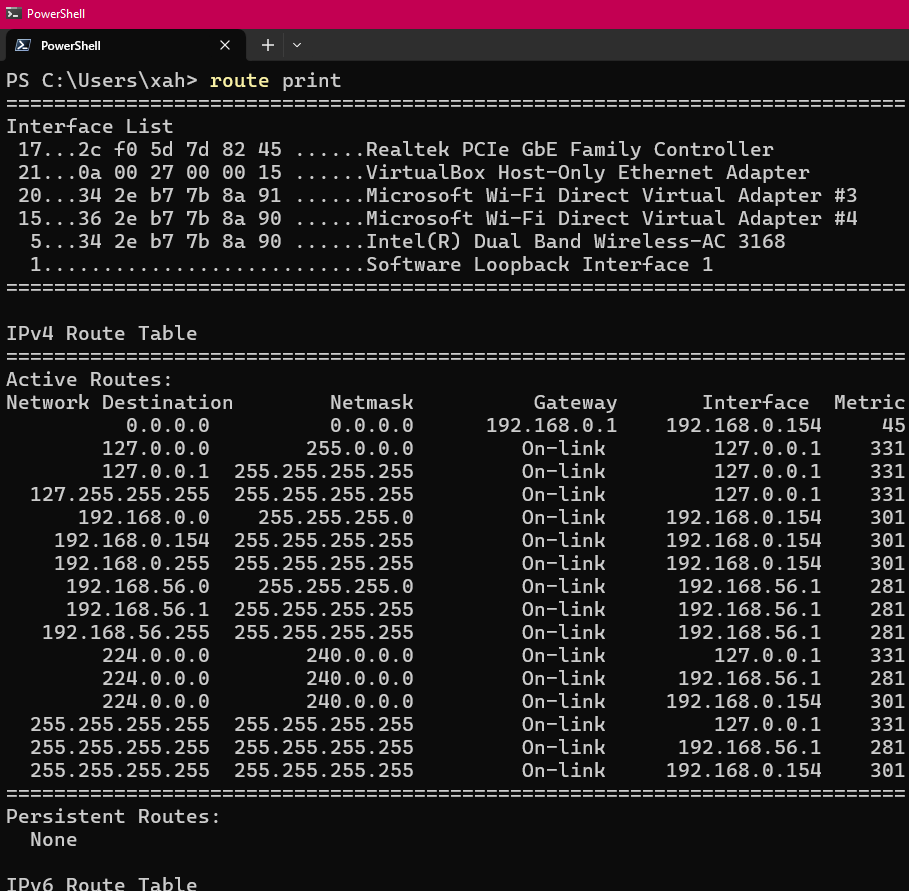
route print
The column “Gateway” shows the IP address of router.
List MAC Address of All Network Adapters (NIC)
ipconfig /all
Each block of text is a network adapter.
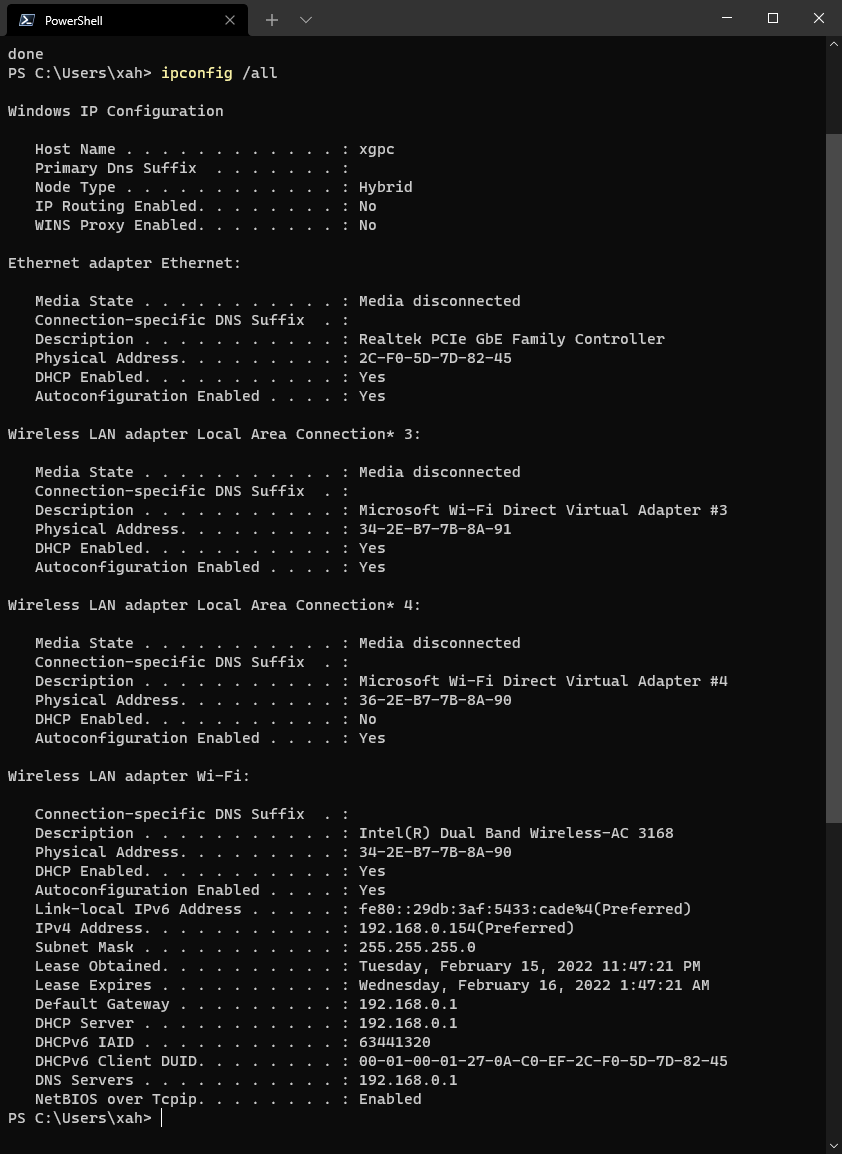
Show MAC Address of Network Adapter
ipconfig /all
The line “Physical Address” shows the MAC address of that network adapter on your machine.
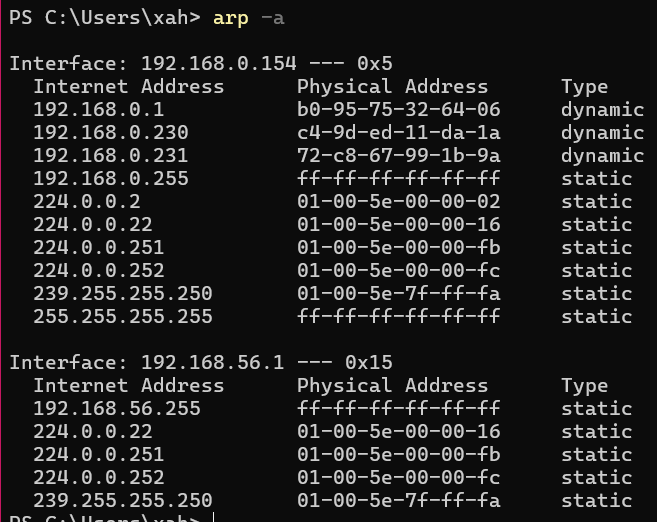
Show MAC Address of Router
first, find the ip address of the router.
then, use arp
# show a table of IP address and its corresponding MAC address arp -a
What is ipconfig
ipconfig is most useful internet config tool.
# show help ipconfig /?
ipconfig /?
USAGE:
ipconfig [/allcompartments] [/? | /all |
/renew [adapter] | /release [adapter] |
/renew6 [adapter] | /release6 [adapter] |
/flushdns | /displaydns | /registerdns |
/showclassid adapter |
/setclassid adapter [classid] |
/showclassid6 adapter |
/setclassid6 adapter [classid] ]
where
adapter Connection name
(wildcard characters * and ? allowed, see examples)
Options:
/? Display this help message
/all Display full configuration information.
/release Release the IPv4 address for the specified adapter.
/release6 Release the IPv6 address for the specified adapter.
/renew Renew the IPv4 address for the specified adapter.
/renew6 Renew the IPv6 address for the specified adapter.
/flushdns Purges the DNS Resolver cache.
/registerdns Refreshes all DHCP leases and re-registers DNS names
/displaydns Display the contents of the DNS Resolver Cache.
/showclassid Displays all the dhcp class IDs allowed for adapter.
/setclassid Modifies the dhcp class id.
/showclassid6 Displays all the IPv6 DHCP class IDs allowed for adapter.
/setclassid6 Modifies the IPv6 DHCP class id.
The default is to display only the IP address, subnet mask and
default gateway for each adapter bound to TCP/IP.
For Release and Renew, if no adapter name is specified, then the IP address
leases for all adapters bound to TCP/IP will be released or renewed.
For Setclassid and Setclassid6, if no ClassId is specified, then the ClassId is removed.
Examples:
> ipconfig ... Show information
> ipconfig /all ... Show detailed information
> ipconfig /renew ... renew all adapters
> ipconfig /renew EL* ... renew any connection that has its
name starting with EL
> ipconfig /release *Con* ... release all matching connections,
eg. "Wired Ethernet Connection 1" or
"Wired Ethernet Connection 2"
> ipconfig /allcompartments ... Show information about all
compartments
> ipconfig /allcompartments /all ... Show detailed information about all
compartments
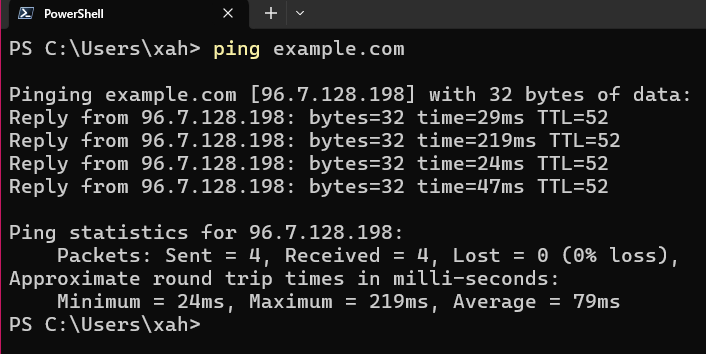
ping

# show help ping /?
ping /?
Usage: ping [-t] [-a] [-n count] [-l size] [-f] [-i TTL] [-v TOS]
[-r count] [-s count] [[-j host-list] | [-k host-list]]
[-w timeout] [-R] [-S srcaddr] [-c compartment] [-p]
[-4] [-6] target_name
Options:
-t Ping the specified host until stopped.
To see statistics and continue - type Control-Break;
To stop - type Control-C.
-a Resolve addresses to hostnames.
-n count Number of echo requests to send.
-l size Send buffer size.
-f Set Don't Fragment flag in packet (IPv4-only).
-i TTL Time To Live.
-v TOS Type Of Service (IPv4-only. This setting has been deprecated
and has no effect on the type of service field in the IP
Header).
-r count Record route for count hops (IPv4-only).
-s count Timestamp for count hops (IPv4-only).
-j host-list Loose source route along host-list (IPv4-only).
-k host-list Strict source route along host-list (IPv4-only).
-w timeout Timeout in milliseconds to wait for each reply.
-R Use routing header to test reverse route also (IPv6-only).
Per RFC 5095 the use of this routing header has been
deprecated. Some systems may drop echo requests if
this header is used.
-S srcaddr Source address to use.
-c compartment Routing compartment identifier.
-p Ping a Hyper-V Network Virtualization provider address.
-4 Force using IPv4.
-6 Force using IPv6.
traceroute

tracert /?
Usage: tracert [-d] [-h maximum_hops] [-j host-list] [-w timeout]
[-R] [-S srcaddr] [-4] [-6] target_name
Options:
-d Do not resolve addresses to hostnames.
-h maximum_hops Maximum number of hops to search for target.
-j host-list Loose source route along host-list (IPv4-only).
-w timeout Wait timeout milliseconds for each reply.
-R Trace round-trip path (IPv6-only).
-S srcaddr Source address to use (IPv6-only).
-4 Force using IPv4.
-6 Force using IPv6.
netstat

netstat /?
Displays protocol statistics and current TCP/IP network connections.
NETSTAT [-a] [-b] [-e] [-f] [-n] [-o] [-p proto] [-r] [-s] [-t] [interval]
-a Displays all connections and listening ports.
-b Displays the executable involved in creating each connection or
listening port. In some cases well-known executables host
multiple independent components, and in these cases the
sequence of components involved in creating the connection
or listening port is displayed. In this case the executable
name is in [] at the bottom, on top is the component it called,
and so forth until TCP/IP was reached. Note that this option
can be time-consuming and will fail unless you have sufficient
permissions.
-e Displays Ethernet statistics. This may be combined with the -s
option.
-f Displays Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDN) for foreign
addresses.
-n Displays addresses and port numbers in numerical form.
-o Displays the owning process ID associated with each connection.
-p proto Shows connections for the protocol specified by proto; proto
may be any of: TCP, UDP, TCPv6, or UDPv6. If used with the -s
option to display per-protocol statistics, proto may be any of:
IP, IPv6, ICMP, ICMPv6, TCP, TCPv6, UDP, or UDPv6.
-r Displays the routing table.
-s Displays per-protocol statistics. By default, statistics are
shown for IP, IPv6, ICMP, ICMPv6, TCP, TCPv6, UDP, and UDPv6;
the -p option may be used to specify a subset of the default.
-t Displays the current connection offload state.
interval Redisplays selected statistics, pausing interval seconds
between each display. Press CTRL+C to stop redisplaying
statistics. If omitted, netstat will print the current
configuration information once.
route
route is a command used to view and manipulate the TCP/IP routing table. Manual manipulation of the routing table is characteristic of static routing.
route /?
Manipulates network routing tables.
ROUTE [-f] [-p] [-4|-6] command [destination]
[MASK netmask] [gateway] [METRIC metric] [IF interface]
-f Clears the routing tables of all gateway entries. If this is
used in conjunction with one of the commands, the tables are
cleared prior to running the command.
-p When used with the ADD command, makes a route persistent across
boots of the system. By default, routes are not preserved
when the system is restarted. Ignored for all other commands,
which always affect the appropriate persistent routes. This
option is not supported in Windows 95.
-4 Force using IPv4.
-6 Force using IPv6.
command One of these:
PRINT Prints a route
ADD Adds a route
DELETE Deletes a route
CHANGE Modifies an existing route
destination Specifies the host.
MASK Specifies that the next parameter is the 'netmask' value.
netmask Specifies a subnet mask value for this route entry.
If not specified, it defaults to 255.255.255.255.
gateway Specifies gateway.
interface the interface number for the specified route.
METRIC specifies the metric, ie. cost for the destination.
All symbolic names used for destination are looked up in the network database
file NETWORKS. The symbolic names for gateway are looked up in the host name
database file HOSTS.
If the command is PRINT or DELETE. Destination or gateway can be a wildcard,
(wildcard is specified as a star '*'), or the gateway argument may be omitted.
If Dest contains a * or ?, it is treated as a shell pattern, and only
matching destination routes are printed. The '*' matches any string,
and '?' matches any one char. Examples: 157.*.1, 157.*, 127.*, *224*.
Pattern match is only allowed in PRINT command.
Diagnostic Notes:
Invalid MASK generates an error, that is when (DEST & MASK) != DEST.
Example> route ADD 157.0.0.0 MASK 155.0.0.0 157.55.80.1 IF 1
The route addition failed: The specified mask parameter is invalid. (Destination & Mask) != Destination.
Examples:
> route PRINT
> route PRINT -4
> route PRINT -6
> route PRINT 157* .... Only prints those matching 157*
> route ADD 157.0.0.0 MASK 255.0.0.0 157.55.80.1 METRIC 3 IF 2
destination^ ^mask ^gateway metric^ ^
Interface^
If IF is not given, it tries to find the best interface for a given
gateway.
> route ADD 3ffe::/32 3ffe::1
> route CHANGE 157.0.0.0 MASK 255.0.0.0 157.55.80.5 METRIC 2 IF 2
CHANGE is used to modify gateway and/or metric only.
> route DELETE 157.0.0.0
> route DELETE 3ffe::/32
arp, Address Resolution Protocol, IP to MAC address

arp /?
Displays and modifies the IP-to-Physical address translation tables used by
address resolution protocol (ARP).
ARP -s inet_addr eth_addr [if_addr]
ARP -d inet_addr [if_addr]
ARP -a [inet_addr] [-N if_addr] [-v]
-a Displays current ARP entries by interrogating the current
protocol data. If inet_addr is specified, the IP and Physical
addresses for only the specified computer are displayed. If
more than one network interface uses ARP, entries for each ARP
table are displayed.
-g Same as -a.
-v Displays current ARP entries in verbose mode. All invalid
entries and entries on the loop-back interface will be shown.
inet_addr Specifies an internet address.
-N if_addr Displays the ARP entries for the network interface specified
by if_addr.
-d Deletes the host specified by inet_addr. inet_addr may be
wildcarded with * to delete all hosts.
-s Adds the host and associates the Internet address inet_addr
with the Physical address eth_addr. The Physical address is
given as 6 hexadecimal bytes separated by hyphens. The entry
is permanent.
eth_addr Specifies a physical address.
if_addr If present, this specifies the Internet address of the
interface whose address translation table should be modified.
If not present, the first applicable interface will be used.
Example:
> arp -s 157.55.85.212 00-aa-00-62-c6-09 .... Adds a static entry.
> arp -a .... Displays the arp table.
